Recently, I’m getting an increased number of requests if the package offered by MAGIX for digitization and archiving of old video tapes is any good.
As technician at the National Video-Archive, I probably have certain demands regarding digitization quality and archive suitability of video material, which might seem “overkill” for most end-users (e.g. lossless codecs).
In order to produce digital copies of analog videos, this product might hardly be underbid.
Yet, I strongly question the long-term archiving properties (and quality) of the output formats of the MAGIX suite.
I’ve done some research regarding this MAGIX product, and I’ve encountered several things that one should know/consider, before buying this product.
Summary / Overview
- Questionable quality of the analog/digital (A/D) converter
- Exclusively lossy output formats
- WMV, as well as optical carriers (DVD, Blu-Ray, etc) are absolutely inadequate as archive format
- Unclear number of generation losses during record/editing/export
Possible alternative hybrid solution:
Use the MAGIX A/D converter stick with VirtualDub (see below) and FFV1 or DV as video codec. PCM uncompressed for audio.
Store the original export files on harddisks and DVD/Blu-Ray only for access copies.
This enables you to re-create DVD/Blu-Rays later on, in case they decay. Or convert your videos in the future to “then-common” video formats for viewing.
Without additional generation loss.
Supported audio/video formats:
Under “Technical Data > Data Formats“, a list of supported formats for video/audio/image are listed.
The formats listed there are only listed according to their file suffixes (e.g. AVI, MOV, MP3, OGG). This may seem simple(r) on first sight, but it’s lacking concrete information about the actually supported codecs.
A video file always consists (at least) of 3 components:
- container
- video-codec
- audio-codec
Despite the fact, that the list of video formats given by MAGIX is a mixture of container formats (AVI/MOV) and codecs (DV, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, WMV), the only format for file-export is “WMV(HD)”.
Additionally, there is no information given about how the audio is stored.
The list of audio formats only lists lossy (!) codecs like MP3/WMA/Vorbis for import.
Analog-digital (A/D) converter:
The analog video signal is being converted using a small, sweet USB-stick with video inputs.
I was not able to find publicly accessible information about technical details about this converter.
Open questions:
- Does the A/D converter provide the uncompressed digital signal – or only the already lossy compressed version?
- Same question for audio…
- Does it preserve video fields accurately?
- Does it preserve color information, or the chroma subsampling (e.g. 4:2:2 to 4:2:0)?
Although the A/D converter stick seems to be usable by other video applications (e.g. VirtualDub), it’s unclear if recording to another codec already contains a generation loss.
This would be very relevant for eventual post-editing (e.g. cropping, color corrections, audio corrections, etc), since one would be to accept at least 3 generation losses:
- Loss #1: Lossy compression in A/D converter
- Loss #2: Image-/audio-recording in lossy codec (WMV/WMA?)
- Loss #3: Export to a lossy format (DVD, Blu-Ray, etc)
UPDATE (26.Aug.2015):
I was told by a user that the program provided an export to MPEG-2 in recent versions.
Unfortunately, this “program bug” was “fixed” by MAGIX.
Quote MAGIX support (Translated from German to English):
“If MPEG-2 was listed as export option, that is a bug which was corrected automatically with the next program start.
So there is no possibility to export the video as MPEG-2. Additionally, this function can also not be activated.”
MAGIX support also gave us the tip that the MPEG, generated by the A/D converter stick, would intermediately be stored in the “My Record” folder.
At least with this option, you would have had only one generation loss.
Unfortunately, this “program bug” was also “fixed”:
The original MPEG-2 is not accessible any more – the video is now transcoded directly to a 16:9 WMV/WMA format.
So in the current version, this adds another 2 quality losses:
- Loss #4: Interpolation by upscaling from SD to HD (720×576 auf 1920×1080)
- Loss #5: If there are no black borders added left/right, then cropping occurs
I hope that at least the audio is stored lossless (e.g. uncompressed PCM) before export.
Yet, this is uncertain.
For those who would (still) like to copy and preserve their videos in a safe(r) way, I’ve written down some options and background informations here:
Formats (more) suitable for archiving:
The best option, of course, is if you can store audio/video uncompressed or in a mathematically lossless codec (e.g. FFV1).
Currently, this might still be an issue for end-users, due to the rather huge data size (compared to lossy).
For example, FFV1/PCM in AVI requires about 90 GB for 4h VHS (~370 MB/min).
Of course it’s tempting to have smaller files – but that has its price.
In case one decides to use compression without any loss, any other codec than Windows Media is to be preferred. Due to its Microsoft origin, WMV/WMA is strongly bound to Windows, and due to this format’s licensing- und patent-obstacles it’s unclear if (and under which conditions) one is able to open these formats in the future.
For Non-Windows environments, the license costs for creators of applications/devices that can play (or convert) WMV is currently at 300.000 USD per year.
See: “Windows Media Components Product Agreement, page 12.
The best compromise would probably be “DV” (=lossy, but widespread open standard) as video codec and PCM (=uncompressed. Quasi “WAV”) for audio in AVI. That would approximately be 55 GB for 4h VHS (~230 MB/min).
Within a reasonable value-for-money range, a A/D converter like the ADVC55 might make sense.

As recording program “VirtualDub” could be used.
Audio should be recorded uncompressed (PCM) – and also stored in that format in the video container file.
Presets for recording DV in the most exact way can be downloaded here.
These settings are part of DVA-Profession, and are used at the Austrian Mediathek (the National Audio/Video Archive).
A general rule of thumb for long-term preservation of media formats is, that the implementation of an open format/standard under a Free Software license (e.g. GPL) has the highest chance to “virtually immortal”.
For example, if a media format is supported by the tool “FFmpeg“, your changes are very good 🙂
DVD/Blu-ray as physical carrier:
Here a short quote from the product page (Translated from German to English):
“Digital is better: Advantages of DVDs & Blu-ray Discs In addition to the large disk space, long service life, and small size, they do not have any sensitive mechanical components, making them ideal for archiving!”
Of course, the part about the mechanical components is correct, but saying it’s “ideal for archiving?
Theoretically “yes” – practically “no”.
The times where archives stored everything on optical carriers are long gone.
Mainly, because it has quickly shown that self burned optical carriers are way more fragile and short-lived than analog material, hard disks or magnetic tapes.
Burned disks that are not readable without errors after 2 years are not the exception. The higher the density of the carrier, the more fragile of course are is the data stored on it…
Furthermore one should distinguish between “data disk” and “video disk” – the same applies to CD, as well as DVD and Blu-Ray.
If one stores their videos on a video-disk (e.g. Video-DVD), the audio/video format – including resolution and aspect ratio – is mostly fixed.
Currently, these are exclusively lossy video codecs:
- CD: MPEG-1
- DVD: MPEG-2
- Blu-Ray: MPEG-4 (H.264)
At the moment, there is (currently) no perfect carrier. Especially not for digital data.
For the time being, I would suggest to store the originally captured files on hard disks – and a copy on DVD/Blu-Ray only as access copy.
This allows to choose the archiving format separately from the access format, increasing ones chances to more easily and without additional generation loss convert the videos for viewing.
Aspect ratio:
Analog video is stored in “standard definition” (SD) resolution, and was always recorded with the aspect ratio of 4:3 – and that’s also the way the image is stored on the tape.
In screenshots on the MAGIX Website however, the video is exclusively displayed in 16:9:
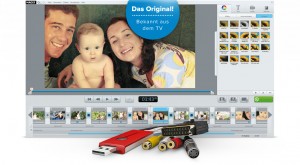
Even if you have black borders at top/bottom (=<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letterboxing_(filming)"), the information on the tape originally isn't wide screen at all.
In Europe we have PAL as TV-/video norm.
If you digitize PAL-SD video, that usually results in a pixel resolution of 720×576. Due to quadratic pixel aspect ratio (PAR), that relates to 5:4 storage aspect ratio (SAR).
Even if one originally recorded 16:9 on e.g. DV (=”Digital Video”) or Digital Betacam, it is stored anamorph with 720×576 pixels (=5:4) – also not wide screen.
If 4:3 is stored as 16:9 full screen, information is always lost.
How does the MAGIX Rescue Your Videotapes handle that?
Does it automatically crop, or could one have black borders left/right (=”pillarbox“) instead?
That would at least offer a lossless video image format for archiving, in case one wants to convert to a 16:9 aspect ratio for viewing (e.g. Blu-Ray/HD).
I don’t even dare to ask how fields (half-images of a frame) and/or deinterlacing are handled…
MXV:
Justa short remark regarding the “MXV” format for video:
At my work at the national video archive, we encounter a variety of most diverse video formats as source. Until today, MXV was unknown to me.
During my recherche, I wasn’t able to find technical details about it, except of these:
- It’s a MAGIX-internal format. Probably a container or project format
- There are probably no tools (except for MAGIX’) that can open/convert it
- It seems to store video in lossy-only formats (MPEG-2)
- Which audio format is uses is completely unclear. PCM? MP3? WMA? MXA?
If you should have stored your videos in this format, I suggest to export/convert it to an open format as soon as possible. It is absolutely unclear if (and what-with) one can open MXV in the future at all.
Unfortunately, it is not impossible that one loses quality during that conversion (due to additional, lossy compression during export).
Please don’t send complaints to me, but to MAGIX 😉


